Details Of Published TSH Receptor Mutation
Gly 132 Arg
c.394G>CInactivating TSH Receptor Mutation
Type
loss
Manifestation
family
Exon
4
Legend:

Male

Female

Unknown

Deceased
+
Mutation
-
Wild-Type

Heterozygous

Heterozygous

Compound Heterozygous

Homozygous

Hypothyroid

Hypoplastic Gland + Hypothyroid
P
Index Patient
Molecular Characteristics:
Narumi et al.
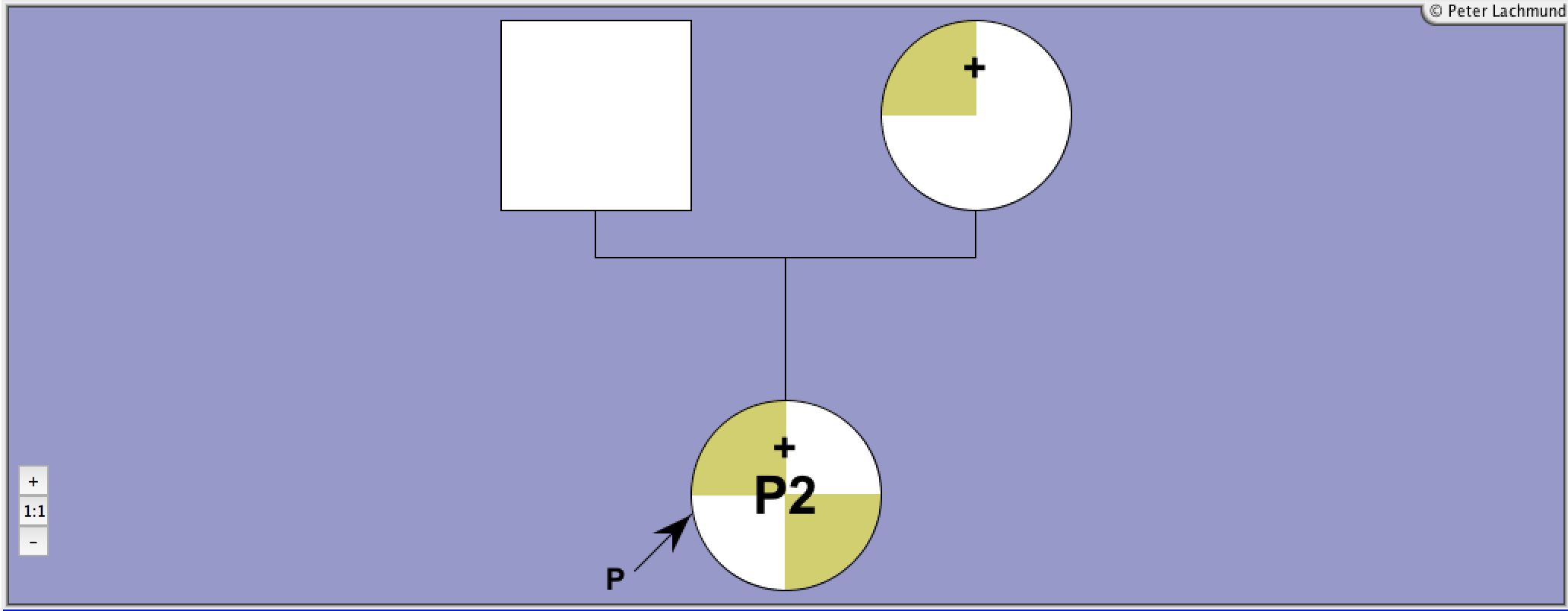
Patient 2: compound heterozygous
Gly132Arg/Arg450His
mother: Gly132Arg/wt
Patient 2: compound heterozygous
Gly132Arg/Arg450His
mother: Gly132Arg/wt
Clinical Features:
Narumi et al.
mild thyroid hypoplasia
diagnosed at 6yr, TSH elevated
mild thyroid hypoplasia
diagnosed at 6yr, TSH elevated
Treatment:
L-T4
Functional Characteristics:
cAMP
(basal)
(basal)
cAMP
(TSH)
(TSH)
IP
(basal)
(basal)
IP
(TSH)
(TSH)
TSH-Binding
Cell Surface Expression
Prevalence
LRA
Ref
2
Legend:
cAMP (basal): basal in vitro cAMP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
cAMP (TSH): maximal in vitro cAMP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
IP (basal): basal in vitro IP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
IP (TSH): maximal in vitro IP production of mutant over wild-type TSHR
TSH-binding: maximal TSH-binding compared to the wild-type TSHR
Cell surface expression: cell surface expression of mutant compared to WT-TSHR
LRA: linear regression analysis (LRA) of constitutive activity as a function of TSHR expression determined by 125I-bTSH binding or FACS analysis compared to the wild-type TSHR
Prevalence: Prevalence of (somatic and germline) activating mutations*
Ref: Reference for functional characterization
Child: Found in children.
Reference 1:
Lee et al.
Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 75:715-721.
Molecular screening of the TSH receptor (TSHR) and thyroid peroxidase (TPO) genes in Korean patients with nonsyndromic congenital hypothyroidism.
2011
Reference 2:
Narumi et al.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:1317-1323.
TSHR mutations as a cause of congenital hypothyroidism in Japan: a population-based genetic epidemiology study.
2009